Solution
-
Capacitor Kits Electronic Components Distributor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as a condenser,[1] a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the condenser microphone.
-
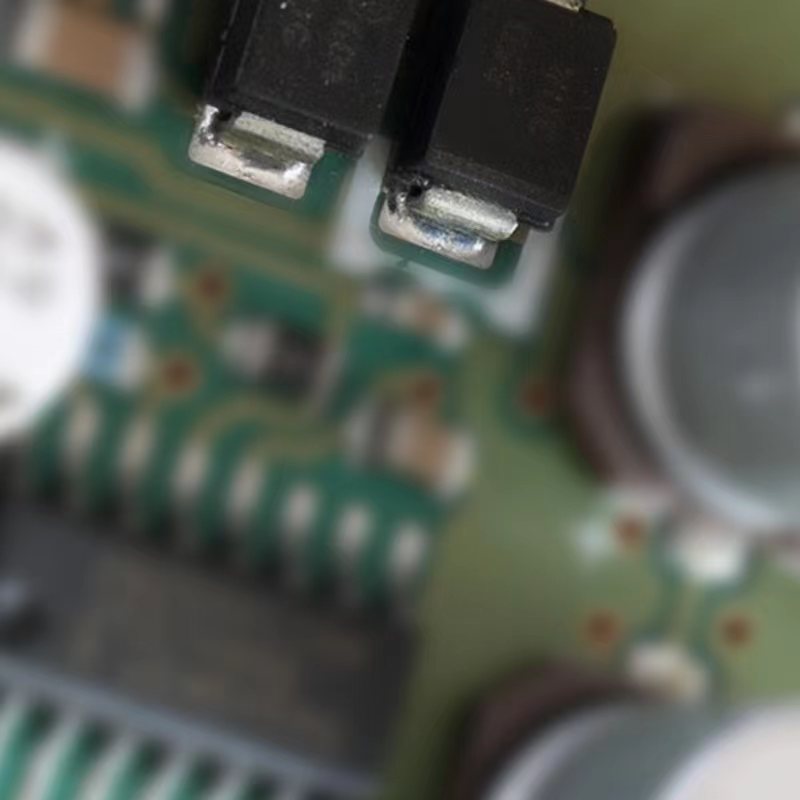

High Speed Switching Diodes and High Voltage Switching Diodes Sourcing
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate.
-
Mosfet purchase service for switching circuits
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. A metal-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MISFET) is a term almost synonymous with MOSFET. Another synonym is IGFET for insulated-gate field-effect transistor.
The basic principle of the field-effect transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925.[1]
-
Efficient Resistors customized sourcing solutions
Products within this category include fixed-value (non-adjustable) resistors and related mounting accessories, organized according to their physical form factor or the method by which they are physically and electrically connected within an end application. Adjustable or variable-value resistors (also known as potentiometers or rheostats) are found separately, in a category of their own.
-
Authorized Distributor for Transistor Manufacturer of Electronic Components
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electrical signals and power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics.[1] It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor’s terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.
-
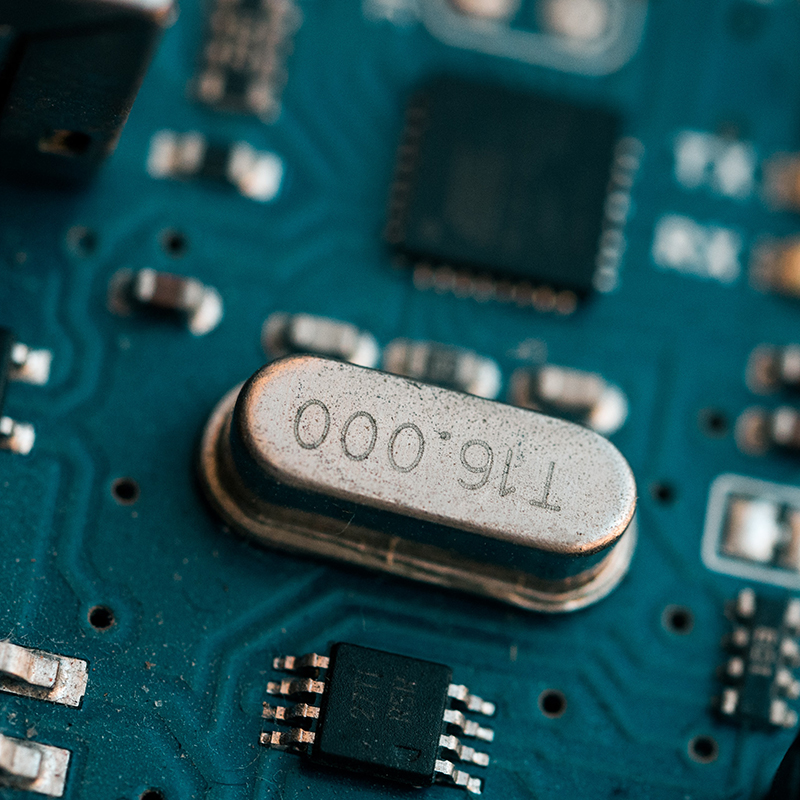

Crystals, Oscillators, Resonators Distributor with
Crystal, oscillator, and resonator products are devices used as sources or references for frequency generation and time measurement. Based in most cases on the physical vibration of some mechanical structure that vibrates at a known frequency, they are further classified along lines of their specific implementation and the degree to which additional supporting functions are incorporated, enabling convenience of use or higher attainable degrees of precision and/or accuracy.






